Industrial cogeneration
Industrial cogeneration, also known as co-generation, is an innovative process for using energy that offers many benefits for businesses and the environment. Cogeneration is a technological process in which heat and electricity are produced simultaneously. Less fuel is used to produce the same amounts of electricity and heat than in separate production, resulting in both more efficient use of fuel and a reduction in global CO2 emissions into the atmosphere.
COGENERATION: EFFICIENCY AND SUSTAINABILITY
Cogeneration, also known as co-generation, is an efficient fuel utilization process that offers many benefits for businesses and the environment. The generation facility allows the simultaneous production of electricity and heat from a single source, leading to increased energy efficiency and reduced costs. In this article we will take a closer look at cogeneration, its applications and the benefits it brings.
WHAT IS COGENERATION?
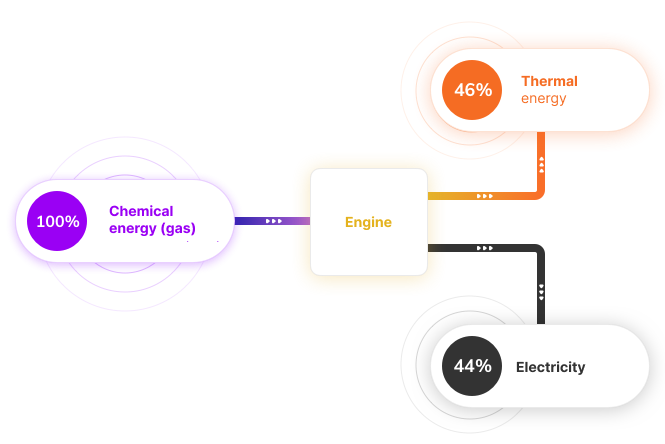
Cogeneration is a process in which energy is produced simultaneously in the form of electricity and heat from a single energy source. The main source of cogeneration is usually an internal combustion engine or gas turbine. The heat released in the electricity generation process is then used for thermal purposes, such as heating buildings, producing steam or cooling. This unique combination maximizes the use of the energy contained in the fuel and minimizes losses. Importantly – CHP can be powered by a wide range of fuels – coal, natural gas, biomethane, as well as hydrogen. An unquestionable advantage of CHP is the high efficiency of CHP units (up to 91%) and compact and modular design.
COGENERATION APPLICATIONS
Cogeneration is widely used in various sectors and industries. Here are some examples:
- Chemical and petrochemical industry – In this sector, where a large amount of heat is needed for chemical processes, cogeneration allows efficient production of electricity and supply of heat for technological processes.
- Food industry – CHP can be used as the primary source of electricity generation for food production by powering machinery and providing heat for pasteurization and drying processes.
- Paper industry – In the paper industry, CHP can provide the electricity needed to power machinery and provide heat for paper drying.
- District heating and cooling – CHP can provide heat for heating buildings in cities, preparing hot water and heating water in local swimming pools, while also producing electricity.
- Pharmaceutical industry – In the pharmaceutical sector, where precise temperature control is essential, CHP can provide a reliable heat source.
Benefits of INDUSTRIAL COGENERATION
Industrial cogeneration has numerous benefits:
- Energy efficiency – With cogeneration, the energy contained in the fuel is maximized, leading to savings and increased energy efficiency.
- Cost savings – Producing its own electricity and heat allows it to reduce the cost of purchasing energy from outside (the customer does not bear at least the variable costs of distribution services for the electricity it generates and consumes)
- Sustainability – Industrial cogeneration is more environmentally friendly, as it reduces emissions of harmful greenhouse gases, which makes it possible to obtain support in the form of grants or loans from national and European funds.
- Reliability of energy supply – Having your own energy source increases the reliability of supply, increases energy security and minimizes the risk of supply interruptions.
Why it's important:
Combined heat and power (CHP) is an efficient way of producing energy that brings significant economic and environmental benefits. It provides for the energy needs of various industries while supporting sustainable development goals and enhancing energy security. Therefore, more and more companies and local government units are beginning to consider implementing cogeneration in order to be more competitive and environmentally friendly.
